AB AP and lateral radiographs showing the original proximal radius
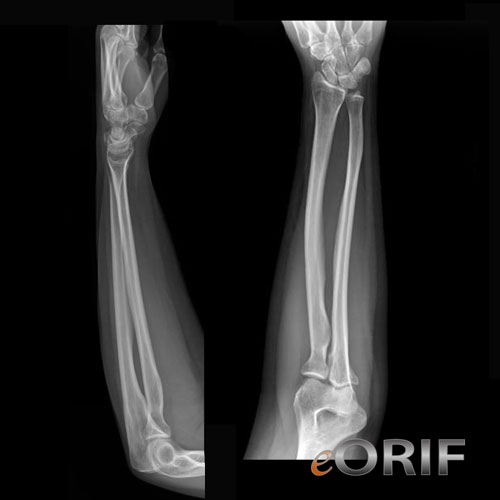
Forearm Xray eORIF
Both Bone Forearm Fractures are one of the most common pediatric fractures, estimated around 40% of all pediatric fractures. Diagnosis is made with plain radiographs of the forearm. Treatment is closed reduction and casting for the majority of fractures. Surgical intervention is indicated for significantly displaced or angulated fractures in.
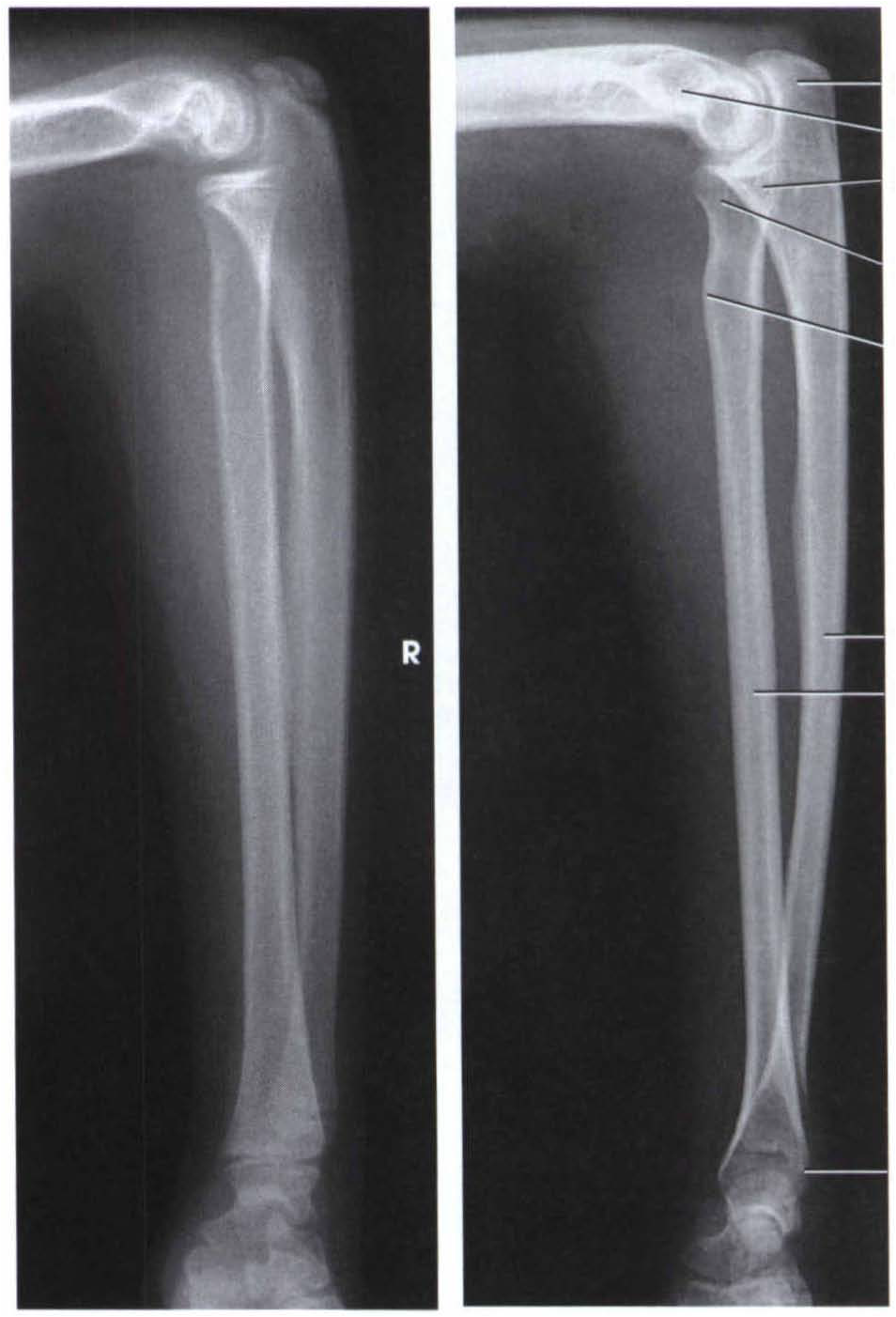
Gudang Medis teknik radiografi antebrachii
This view demonstrates the elbow joint in its natural anatomical position allowing for assessment of suspected dislocations or fractures and localizing foreign bodies within the forearm. patient is seated alongside the table forearm is supinated, and its dorsal surface is kept in contact with the cassette with extension at the elbow joint

Forearm X Ray Anatomy
Radius and ulnar shaft fractures, also known as adult both bone forearm fractures, are common fractures of the forearm caused by either direct trauma or indirect trauma (fall). Diagnosis is made by physical exam and plain orthogonal radiographs. Treatment is generally surgical open reduction and internal fixation with compression plating of.

Forearm Radiograph Radiology student, Medical radiography, Medical
Anatomy . The brachialis muscle originates from the front of your humerus, or upper arm bone.It arises from the distal part of the bone, below your biceps brachii muscle. It then courses down the front of your arm, over your elbow joint, and inserts on the coronoid process and tuberosity of your ulna.The brachialis muscle, along with the supinator muscle, makes up the floor of the cubital.

Image
An observational study has been performed using US imaging to measure brachial and antebrachial fasciae thickness at anterior and posterior regions, respectively, of the arm and forearm at different levels with a new protocol in a sample of 25 healthy volunteers. Results of fascial thickness revealed statistically significant differences ( p.

ANTEBRACHII FRACTURE PDF
Overview. An X-ray is a quick, painless test that produces images of the structures inside your body — particularly your bones. X-ray beams pass through your body, and they are absorbed in different amounts depending on the density of the material they pass through. Dense materials, such as bone and metal, show up as white on X-rays.

forearm skeletal anatomy radiology
Describe the common presentation of a patient with forearm fractures. Identify the various radiological investigations required for diagnosing forearm fractures. Explain the various treatment options for patients with forearm fractures, along with the complications anticipated. Access free multiple choice questions on this topic. Go to:
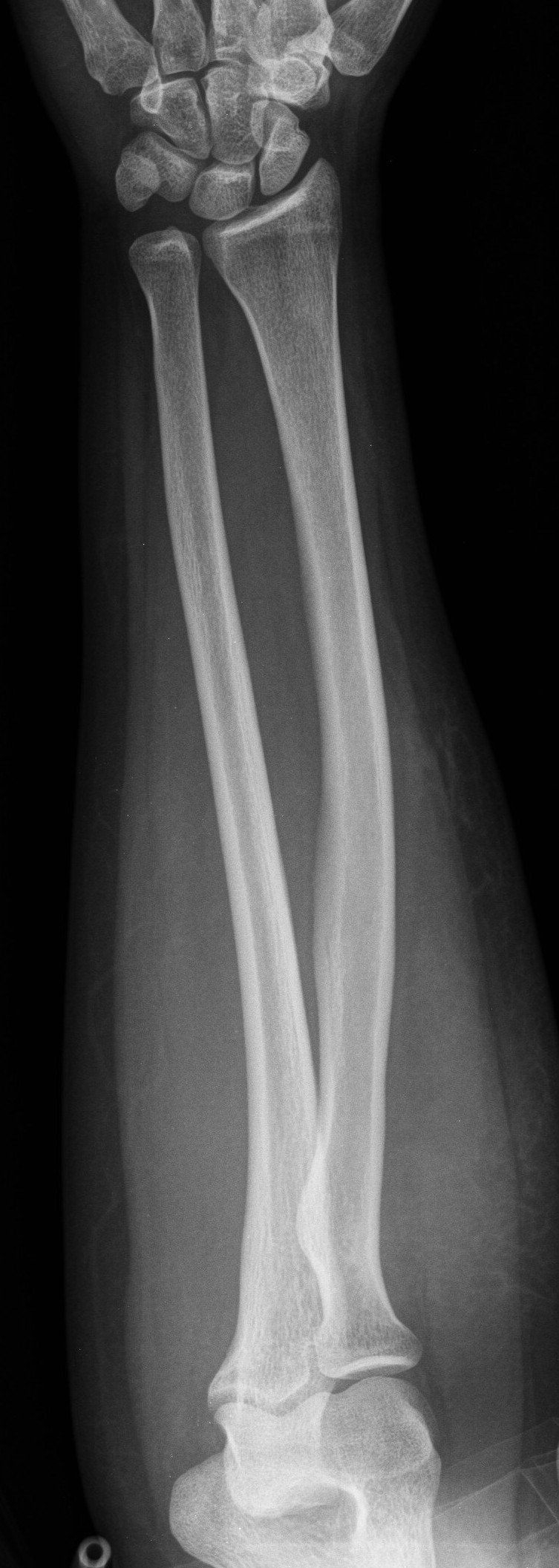
UCSD Musculoskeletal Radiology
Hand, humeral and antebrachii X-ray showed no fracture nor dislocation. Electromyography (EMG) test showed no nerve conduc- tion velocity of left axillary nerve injury. Patient underwent physio- therapy and given neuroprotectors. After 7 days, there was a significant improvement in shoulder abduction and left arm prona- tion.

Pin by Tracey Burns on Radiology Diagnostic imaging, Radiology
The trauma dated of 1 day and X-ray was initially judged normal in the emergency department. Due to the persistence of the pain and the functional impotence, the patient presented again to our.

Show Me A Picture Of A XRay imgultra
fracture location (extra-, juxta- or intra-articular) degree of angulation degree of displacement carpus ensure no carpal malalignment or fractures are present assess articulation of radio-lunate and radio-scaphoid joint
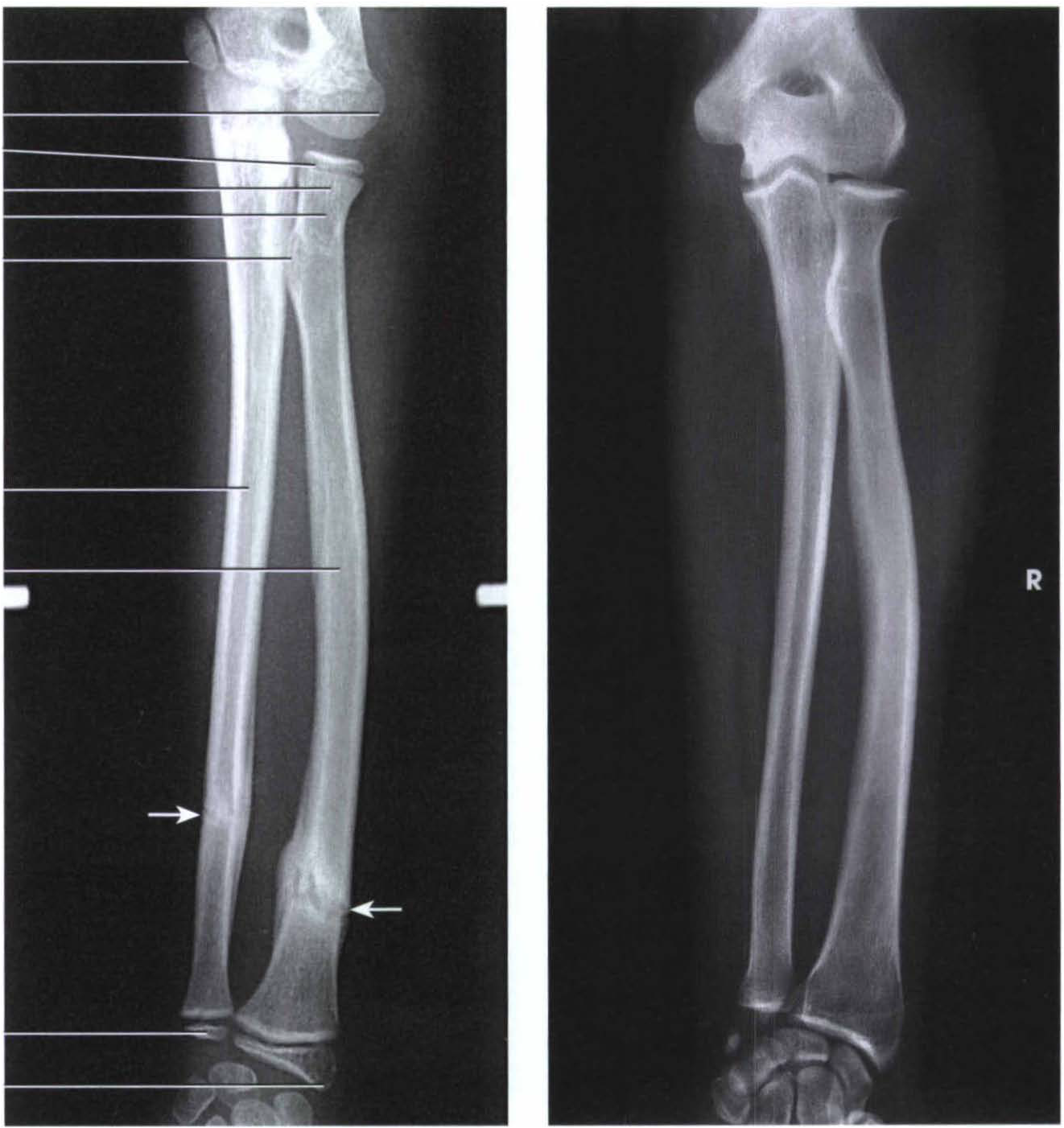
Gudang Medis teknik radiografi antebrachii
50-60 kVp 2-5 mAs SID 100 cm grid no Image technical evaluation the elbow is in an AP position, with slight internal rotation. patient's arm should be rotated externally to ensure that the trochlea and capitulum are seen in profile. Practical points At times, patients may not be able to fully extend their elbow joint.

Some anatomy for the basic forearm radiographs! Kevin GrepMed
Presentation Fall from bike. Pain in wrist. Patient Data Age: 9 years Gender: Male x-ray Frontal Lateral Normal examination. No fracture. No joint effusion. Case Discussion Forearm x-rays are difficult. You end up with an frontal view of the wrist and a lateral view of the elbow on one image and the opposite on the other.

AB AP and lateral radiographs showing the original proximal radius
OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this article is to review the anatomy, biomechanics, and multimodality imaging findings of common and uncommon distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ), triangular fibrocartilage complex, and distal ulna abnormalities. CONCLUSION. The DRUJ is a common site for acute and chronic injuries and is frequently imaged to evaluate chronic wrist pain, forearm dysfunction, and traumatic.

Interpreting Elbow and Forearm Radiographs — Taming the SRU
X-rays are taken to ensure that the reduction was successful. The cast is usually maintained for about 6 weeks. X-ray in cast. Unsuccesful reduction. Guidelines for non-acceptable reduction are (8): Radial shortening > 5 mm; Radial inclination Tilt on lateral projection > 10 degrees dorsal tilt and > 20 degrees volar tilt;
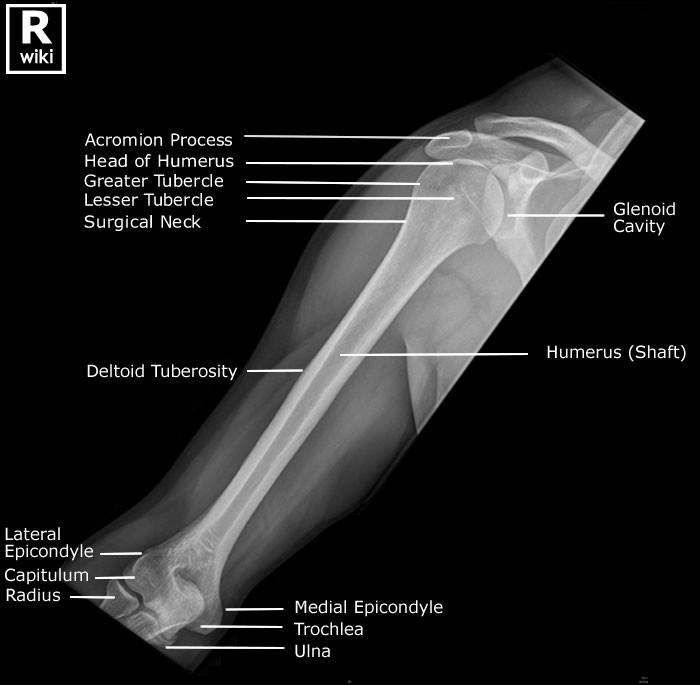
Humerus Radiographic Anatomy wikiRadiography
Also called ambient cistern is a cistern of the subarachnoid space between the posterior end of the corpus callosum and the superior surface of the cerebellum. It is sometimes defined as including the quadrigerminal cistern. On the left a coronal view of the segments of the middle cerebral artery. Horizontal M1-segment.

Radiographs of the left elbow and forearm at 6month followup
Publicationdate 2005-08-23. This article is based on a presentation given by Louis Gilula and adapted for the Radiology Assistant by Ileana Chesaru. First a systematic analysis of the wrist is presented to look for carpal instability and fracture dislocation. Secondly cases are presented as examples in the chapter systematic review and diagnosis.